What is Dyslexia?Simple Definition
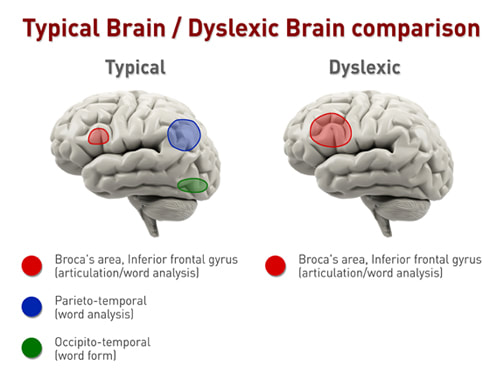
Dyslexia is an inherited condition that makes it extremely difficult to read, write, and spell in your native language—despite at least average intelligence. Revised Definition from the International Dyslexia Association Dyslexia is a neurologically-based, often familial, disorder which interferes with the acquisition and processing of language. Varying in degrees of severity, it is manifested by difficulties in receptive and expressive language, including phonological processing, in reading, writing, spelling, handwriting, and sometimes in arithmetic. Dyslexia is not the result of lack of motivation, sensory impairment, inadequate instructional or environmental opportunities, or other limiting conditions, but may occur together with these conditions. Although dyslexia is lifelong, individuals with dyslexia frequently respond successfully to timely and appropriate intervention. Neurological Differences
|
Some Common Myths Debunked
Myth: Every child who struggles with reading is dyslexic
|
Myth: If a dyslexic child reads out loud for 20 minutes a day, it will improve their reading
Portions of wording and information on this page were used by permission of Susan Barton, BrightSolutions.US |